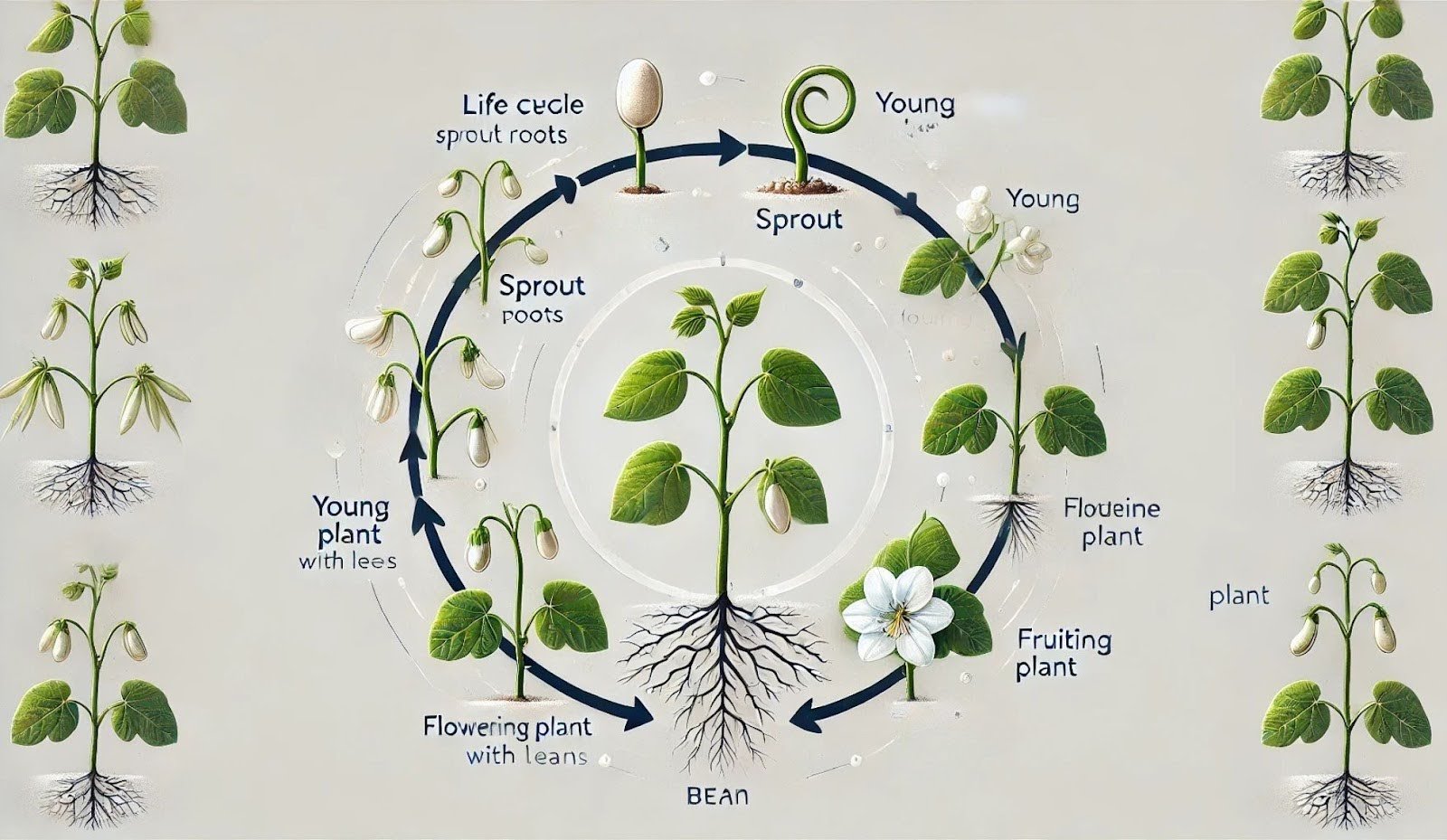
A Life Cycle of a Bean Plant: From Seed to Harvest
A life cycle of a bean plant is a fascinating journey from a tiny seed to a thriving, food-producing plant. Ever wondered how that little bean transforms into a lush green vine covered in pods? It all starts with the right mix of soil, water, and sunlight—then nature works its magic.
From sprouting roots to flowering and finally producing beans, each stage is packed with growth and surprises. Whether you’re planning a backyard garden or an indoor setup, knowing what to expect makes all the difference. Stick around, and let’s dive into the bean plant’s incredible life cycle!
Understanding the Life Cycle of a Bean Plant
Every plant goes through a series of growth stages before it reaches maturity, and bean plants are no exception. From the moment the seed is planted to the time you pick the fresh pods, the bean plant undergoes several important changes. The complete life cycle of a bean plant typically takes 50 to 90 days, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
By understanding each stage, you can make informed decisions about when to water, fertilize, and harvest. Whether you’re growing pole beans, bush beans, or even dwarf varieties for indoor gardens, the basic life cycle remains the same.
The 5 Key Stages of a Bean Plant’s Life Cycle
1. Germination Stage (Day 1-10)

The life of a bean plant begins as a dry, dormant seed. When the right conditions are met—moisture, warmth, and oxygen—the seed begins to sprout. This process, known as germination, is the first and most crucial step in a bean plant’s growth cycle.
During germination, the outer seed coat softens, allowing the embryonic root (radicle) to push downward into the soil. Soon after, the shoot (plumule) emerges, reaching upward toward the light. The first set of leaves, known as cotyledons, provides the young seedling with initial nutrients.
For successful germination, follow these tips:
- Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged.
- Maintain a temperature of 65-85°F (18-30°C) for optimal sprouting.
- If planting indoors, use a damp paper towel method to check viability before planting in soil.
Amend Soil During Germination

Like all vegetables, beans need nutrient-rich soil. When starting a vegetable garden, it is essential to amend the soil and continually replenish its nutrients. Planting bean seeds in good garden soil amended with compost helps the roots find available nutrients immediately. As the roots descend, they pull water and nutrients from the soil into the seed itself. Within a week or so, your bean seeds should sprout, marking the beginning of the seedling stage.
2. Seedling Stage (Day 10-20)
As the young plant emerges, it enters the seedling stage, where it rapidly develops its first true leaves. At this point, the bean plant starts relying on sunlight to produce its own food through photosynthesis.
This stage is critical because young seedlings are delicate and vulnerable to threats like overwatering, damping-off disease, and weak stems. If you’re growing beans indoors, make sure they receive at least 6-8 hours of sunlight or supplement with grow lights.
Here are some care tips for this stage:
- Keep the soil evenly moist but avoid excessive watering.
- Ensure proper air circulation to prevent mold and fungus.
- Use a diluted liquid fertilizer to encourage healthy root development.
By the end of this stage, your bean plant will have established strong roots and be ready for the vegetative growth phase.
3. Vegetative Growth Stage (Day 20-40)
This is the stage where your bean plant experiences rapid growth, producing new leaves, stems, and roots. If you’re growing pole beans, they will start sending out tendrils to climb up supports. Bush beans, on the other hand, will continue growing into compact plants.
During this stage, your plant will need nutrients, adequate water, and proper support. Consider adding compost or a balanced fertilizer (such as 10-10-10 NPK) to encourage lush foliage and strong stems.
Sunlight: Ensure your bean plants get at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but well-draining. Avoid waterlogging, as it can lead to root rot.
Support: If you’re growing pole beans, install stakes, trellises, or bean poles to help them climb.
By the end of this phase, your plant will begin preparing for the next exciting stage—flowering.
4. Flowering Stage (Day 40-60)
As the plant matures, it starts producing small, delicate flowers, usually white, pink, or purple, depending on the variety. These flowers are crucial because they eventually develop into bean pods.
For flowers to turn into pods, pollination must occur. If you’re growing beans outdoors, natural pollinators like bees and butterflies will take care of this. However, if you’re growing beans indoors, you may need to hand-pollinate by gently shaking the flowers or using a small brush to transfer pollen.
Encouraging More Flowers:
- Avoid excessive nitrogen fertilizers, as they promote leafy growth at the expense of flowers.
- Water regularly but avoid splashing water directly on flowers.
- Ensure adequate sunlight exposure.
Once pollination occurs, tiny baby pods start forming at the base of each flower—this means your plant is entering the final stage!
5. Pod Formation & Maturity Stage (Day 60-90)
At this stage, the flowers wither away, leaving behind small pods that continue growing over the next few weeks. These pods will eventually mature into full-sized beans, ready for harvest.
Knowing when to harvest depends on how you plan to use your beans:
For fresh eating (snap beans/green beans): Pick when the pods are still tender and crisp (usually 50-60 days after planting).
For dry beans: Wait until the pods turn yellow and dry out completely (around 90 days).
Regular harvesting encourages the plant to produce more pods, extending your yield.
Gardening With Legumes

Legumes are a great addition to any garden as these plants not only produce food crops, they also fix nitrogen into the soil to improve the earth. Add a few beans to your patch and watch the magic happen above and below the soil.
Factors That Affect Bean Plant Growth
To ensure healthy growth and a high yield, keep these factors in mind:
Soil: Beans grow best in well-draining, loamy soil with a pH between 6.0-7.0.
Sunlight: Beans need full sun (at least 6-8 hours daily) for maximum production.
Watering: Water consistently but avoid standing water. Drip irrigation works best.
Fertilization: Use organic compost or a balanced fertilizer (but avoid excessive nitrogen).
Companion Planting: Grow beans with carrots, cucumbers, or marigolds for pest control.
Common Problems & Solutions in Growing Bean Plants
Growing beans is relatively easy, but you may encounter some issues:
Pests (Aphids, Spider Mites, Bean Beetles): Use neem oil or insecticidal soap to keep them at bay.
Diseases (Powdery Mildew, Root Rot): Ensure good air circulation and avoid overhead watering.
Yellowing Leaves: Could be due to overwatering or nutrient deficiencies—adjust accordingly.
By monitoring your plants closely, you can address problems before they affect your harvest.
Can You Grow Beans Indoors? Absolutely!
If you don’t have outdoor space, beans can thrive indoors with the right setup. Use a deep container (at least 8-12 inches), provide ample sunlight or grow lights, and ensure proper watering. Dwarf or bush varieties are best for indoor growing.
FAQ
How long does a bean plant take to grow?
Most bean plants take 50 to 90 days from seed to harvest, depending on the variety.
What are the main stages in a life cycle of a bean plant?
The five main stages are germination, seedling, vegetative growth, flowering, and pod formation/maturity.
What conditions are best for bean plant growth?
Beans thrive in full sun (6-8 hours daily), well-draining soil, and consistent watering.
Can I grow a bean plant indoors?
Yes! Use a deep container, plenty of light, and proper watering for healthy indoor growth.
How do I speed up bean seed germination?
Soak seeds in warm water for 8-12 hours before planting to speed up sprouting.
How do I know when to harvest beans?
For fresh beans, pick when pods are firm but tender. For dried beans, wait until the pods turn yellow and brittle.
Why are my bean plant’s leaves turning yellow?
It could be overwatering, nutrient deficiency, or disease—check soil moisture and adjust care.
Final Thoughts
By understanding the life cycle of a bean plant, you’ll be well-equipped to grow healthy, productive plants—whether in your backyard or inside your home. With the right care, you’ll soon be enjoying delicious homegrown beans straight from your garden. So, are you ready to start your bean-growing journey? Get planting, and happy gardening!